HandlerMethod
介绍
HandlerMethod是一个基于方法的处理器结构,包含了处理器方法所对应的类和处理器方法,并提供了一些方法参数的访问接口。
分析
1. HandlerMethod顶层接口
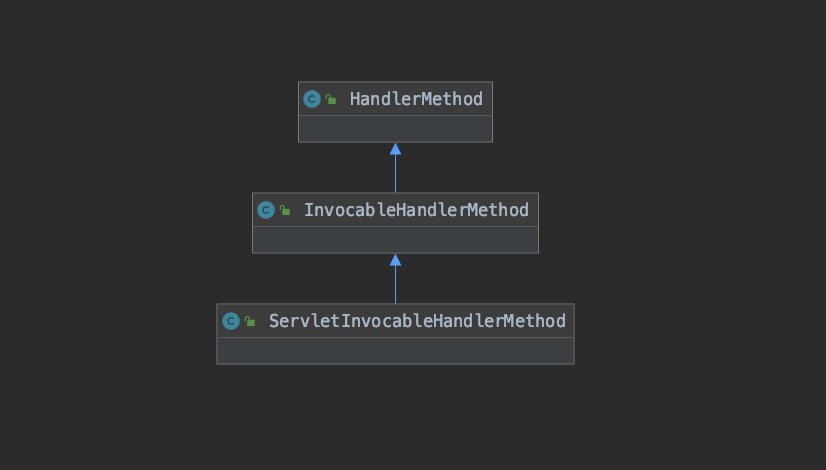
HandlerMethod整体的结构比较简单,但是HandlerMethod并不是设计成接口,直接设计为类,主要用于封装对应的处理方法信息method和这个处理器方法所对应的类信息、这个方法上的所有注解信息等。而真正的处理器方法的处理交由子类InvocableHandlerMethod,这里类包含了参数解析器和参数名称解析器的处理,用于在真正方法调用前进行参数解析。最后底层实现类ServletInvocableHandlerMethod包含了返回值处理器链,用于处理执行处理器方法之后的返回值。
2. 分析
在顶层类HandlerMethod中,主要的实现就是一些构造函数,为了应对不同场景下使用不同的参数对具体的的执行方法进行包装,比如记录具体执行方法的参数、对应的类、对应类的类型、bean工厂、桥接方法等。
在次顶层类InvocableHandlerMethod中,主要添加了参数解析器列表和参数名称解析器列表,用于在支持support()=true的情况下,对参数进行一些个性化处理。并且包含了具体执行方法的反射调用处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| @Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
return doInvoke(args);
}
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod());
try {
return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args);
}catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
assertTargetBean(getBridgedMethod(), getBean(), args);
String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument");
throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError(text, args), ex);
}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException();
if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) targetException;
}else if (targetException instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) targetException;
}else if (targetException instanceof Exception) {
throw (Exception) targetException;
}else {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError("Invocation failure", args), targetException);
}
}
}
|
在ServletInvocableHandlerMethod类中,主要的当处理器方法执行结束后,对返回值的进行一些定制化的特殊处理。springmvc在异步调用的处理上就是通过返回值处理器,当返回值类型为Callable时,进行一些特殊的处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: " + returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);
}
|
注意:参数解析器和返回值处理器在获取时,是获取列表中第一个匹配成功的那个解析器或者处理器,也就是说如果希望定制化的解析器或者处理器被执行到,需要确保它所在的位置之前没有其他的解析器或者处理器会被命中。
